Difference between revisions of "Ellerwald 2.Trift (Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland)"
| [unchecked revision] | [checked revision] |
GameoAdmin (talk | contribs) (CSV import - 20130816) |
GameoAdmin (talk | contribs) (CSV import - 20130823) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[File:Ellerwald%202.Trift.jpg|300px|thumb|right|''Ellerwald 2.Trift (now Adamowo, Poland) | |
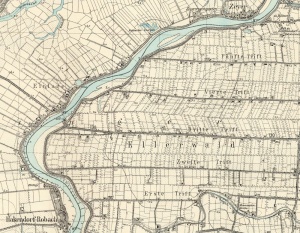
| − | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adamowo,_Elbl%C4%85g_County Wikipedia Commons] | + | Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adamowo,_Elbl%C4%85g_County Wikipedia Commons]'']] [[File:Ellerwald%20detailed%20map.jpg|300px|thumb|right|''Detailed map of Ellerwald 2.Trift, early 20th century. |
| − | + | Source: [http://amzpbig.com/maps/1881_Zeyer_1931.jpg Archiwum Map Zachodniej Polski]'']] Ellerwald 2.Trift (also known as Ellerwald II.Trift and Ellerwald Zweite Trift; now known as Adamowo; coordinates: 54.1608, 19.3292 [54° 9′ 38″ N, 19° 19′ 45″ E]; population in 1905, 226; in 2013, 70) is located approximately 12 kilometres (7 miles) north-west of Elbląg ([[Elbing (Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland)|Elbing]]). | |
| − | |||
| − | Source: [http://amzpbig.com/maps/1881_Zeyer_1931.jpg Archiwum Map Zachodniej Polski] | ||
| − | |||
| − | '']] Ellerwald 2.Trift (also known as Ellerwald II.Trift and Ellerwald Zweite Trift; now known as Adamowo; coordinates: 54.1608, 19.3292 [54° 9′ 38″ N, 19° 19′ 45″ E]; population in 1905, 226; in 2013, 70) is located approximately 12 kilometres (7 miles) north-west of Elbląg ([[Elbing (Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland)|Elbing]]). | ||
During the period of the rule of the Teutonic Knights, the area between the Nogat River and the city of Elbing was covered by marshes, brush, and forest. After the Jagiellonian Channel (Kanał Jagielloński) was constructed in 1483, linking the Elbląg and Nogat rivers, the land was slowly drained and converted into meadows. The development of the meadows began in 1563 when four causeways were built. The land was divided into 435 parcels of land, representing each of the tenement houses in Elbing, and owned by the citizens of Elbing. In order to develop the area, the parcels of land were leased out to Mennonites that had been expelled from the city of Elbing shortly after 1550, along with Mennonites that had been expelled from Ducal Prussia in 1559. In a short period of time, the Mennonites established new villages, including Ellerwald 2.Trift. The land was divided into long strips (Triften), separated by drainage canals. By 1772, Mennonites held approximately 3,500 acres (1,416 hectares) of land in the Ellerwald area. | During the period of the rule of the Teutonic Knights, the area between the Nogat River and the city of Elbing was covered by marshes, brush, and forest. After the Jagiellonian Channel (Kanał Jagielloński) was constructed in 1483, linking the Elbląg and Nogat rivers, the land was slowly drained and converted into meadows. The development of the meadows began in 1563 when four causeways were built. The land was divided into 435 parcels of land, representing each of the tenement houses in Elbing, and owned by the citizens of Elbing. In order to develop the area, the parcels of land were leased out to Mennonites that had been expelled from the city of Elbing shortly after 1550, along with Mennonites that had been expelled from Ducal Prussia in 1559. In a short period of time, the Mennonites established new villages, including Ellerwald 2.Trift. The land was divided into long strips (Triften), separated by drainage canals. By 1772, Mennonites held approximately 3,500 acres (1,416 hectares) of land in the Ellerwald area. | ||
| Line 16: | Line 12: | ||
The Mennonites who lived in the area belonged to the Ellerwald-Elbing Mennonite Church. | The Mennonites who lived in the area belonged to the Ellerwald-Elbing Mennonite Church. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Bibliography = | = Bibliography = | ||
Klassen, Peter J. <em>Mennonites in Early Modern Poland & Prussia</em>. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2009: 41-42. | Klassen, Peter J. <em>Mennonites in Early Modern Poland & Prussia</em>. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2009: 41-42. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 20: | ||
Wolf, Hans-Jürgen. "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Web. 2 February 2013. [http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=1428]. | Wolf, Hans-Jürgen. "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Web. 2 February 2013. [http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=1428]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= Maps = | = Maps = | ||
[[Map:Adamowo, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland|Map:Adamowo, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland]] | [[Map:Adamowo, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland|Map:Adamowo, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland]] | ||
{{GAMEO_footer|hp=|date=February 2013|a1_last=Thiessen|a1_first=Richard D|a2_last=|a2_first=}} | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=|date=February 2013|a1_last=Thiessen|a1_first=Richard D|a2_last=|a2_first=}} | ||
Revision as of 14:31, 23 August 2013

Ellerwald 2.Trift (also known as Ellerwald II.Trift and Ellerwald Zweite Trift; now known as Adamowo; coordinates: 54.1608, 19.3292 [54° 9′ 38″ N, 19° 19′ 45″ E]; population in 1905, 226; in 2013, 70) is located approximately 12 kilometres (7 miles) north-west of Elbląg (Elbing).
During the period of the rule of the Teutonic Knights, the area between the Nogat River and the city of Elbing was covered by marshes, brush, and forest. After the Jagiellonian Channel (Kanał Jagielloński) was constructed in 1483, linking the Elbląg and Nogat rivers, the land was slowly drained and converted into meadows. The development of the meadows began in 1563 when four causeways were built. The land was divided into 435 parcels of land, representing each of the tenement houses in Elbing, and owned by the citizens of Elbing. In order to develop the area, the parcels of land were leased out to Mennonites that had been expelled from the city of Elbing shortly after 1550, along with Mennonites that had been expelled from Ducal Prussia in 1559. In a short period of time, the Mennonites established new villages, including Ellerwald 2.Trift. The land was divided into long strips (Triften), separated by drainage canals. By 1772, Mennonites held approximately 3,500 acres (1,416 hectares) of land in the Ellerwald area.
Until 1772 Ellerwald 2.Trift was located in what was known as Royal Prussia (also known as Polish Prussia) in the Kingdom of Poland. The First Partition of Poland in 1772 resulted in the creation of a new province in 1773, called West Prussia, in which Ellerwald 2.Trift was located. Ellerwald 2.Trift was situated in the district (Kreis) of Elbing until the end of World War I, when it came under the jurisdiction of the German province of East Prussia. At that time the Ellerwald area was inhabited by 736 Mennonites. The village came under the control of Nazi Germany during World War II until February 1945, when it was occupied by Soviet forces and returned to Poland. In 2012 it was a village in the administrative district of Gmina Elbląg, within Elbląg County, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship.
The Prussian census of 1776 lists 10 Mennonite families in Ellerwald 2.Trift with the following surnames: Bock, Dircksen, Kroecker, Loewen, Neusteter, Sawatzki, Thiessen, and Wiens. In 1820, Adamów had 201 residents of whom 57 were Mennonites. At the beginning of the 20th century, the village had 491 hectares and 236 residents.
The Mennonites who lived in the area belonged to the Ellerwald-Elbing Mennonite Church.
Bibliography
Klassen, Peter J. Mennonites in Early Modern Poland & Prussia. Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2009: 41-42.
Stowarzyszenie Konserwatorów Zabytków. "Adamowo." Catalogue of Monuments of Dutch Colonization in Poland. 2005. Web. 2 February 2013. http://holland.org.pl/art.php?kat=obiekt&id=288&lang=en.
Wikipedia. "Adamowo, Elbląg County." Web. 2 February 2013. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adamowo,_Elbląg_County.
Wolf, Hans-Jürgen. "Familienforschung in Westpreußen." Web. 2 February 2013. http://www.westpreussen.de/cms/ct/ortsverzeichnis/details.php?ID=1428.
Maps
Map:Adamowo, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland
| Author(s) | Richard D Thiessen |
|---|---|
| Date Published | February 2013 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Thiessen, Richard D. "Ellerwald 2.Trift (Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland)." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. February 2013. Web. 16 Apr 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Ellerwald_2.Trift_(Warmian-Masurian_Voivodeship,_Poland)&oldid=94488.
APA style
Thiessen, Richard D. (February 2013). Ellerwald 2.Trift (Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland). Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 16 April 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Ellerwald_2.Trift_(Warmian-Masurian_Voivodeship,_Poland)&oldid=94488.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.