Difference between revisions of "Trinidad and Tobago"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
m (Replaced image.) |
m |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
World factbook map '']] | World factbook map '']] | ||
[[File:Trinidad1.jpg|267px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Trinidad_and_Tobago_%28orthographic_projection%29.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | [[File:Trinidad1.jpg|267px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Trinidad_and_Tobago_%28orthographic_projection%29.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | ||
| + | == Introduction == | ||
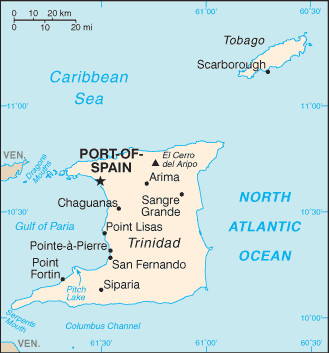
Trinidad and Tobago is a lovely tropical Caribbean twin island nation of 5,131 square kilometers (1,981 square miles) just 11 kilometers from Venezuela. Arawak and Carib Indians inhabited these islands when Christopher Columbus landed there in 1498. African and Indian slaves and indentured servants arrived in these British colonies, which became independent in 1962. A Commonwealth-type parliamentary government was retained with elections held every five years. | Trinidad and Tobago is a lovely tropical Caribbean twin island nation of 5,131 square kilometers (1,981 square miles) just 11 kilometers from Venezuela. Arawak and Carib Indians inhabited these islands when Christopher Columbus landed there in 1498. African and Indian slaves and indentured servants arrived in these British colonies, which became independent in 1962. A Commonwealth-type parliamentary government was retained with elections held every five years. | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
Trinidad's major trading partner was the [[United States of America|United States]] (petroleum, sugar) in 1986. The nation was moving from a primarily rural orientation toward an urban one, and from an agricultural society toward a technological society. Most agricultural work was still performed with hand labor, however. Primary school education was available to all children, but limited facilities and teachers did not permit all children to go on to secondary school. Part of the University of the West Indies was located in Trinidad. In the 1970s educational and health facilities and services were expanded with funds from the oil boom. | Trinidad's major trading partner was the [[United States of America|United States]] (petroleum, sugar) in 1986. The nation was moving from a primarily rural orientation toward an urban one, and from an agricultural society toward a technological society. Most agricultural work was still performed with hand labor, however. Primary school education was available to all children, but limited facilities and teachers did not permit all children to go on to secondary school. Part of the University of the West Indies was located in Trinidad. In the 1970s educational and health facilities and services were expanded with funds from the oil boom. | ||
| + | == Mennonites in Trinidad and Tobago == | ||
[[Mennonite Church (MC)|Mennonite Church (MC)]] [[Broadcasting, Radio and Television|broadcasting]] and medical work, beginning in 1969, led to the formation of the [[Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago|Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago]]. | [[Mennonite Church (MC)|Mennonite Church (MC)]] [[Broadcasting, Radio and Television|broadcasting]] and medical work, beginning in 1969, led to the formation of the [[Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago|Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago]]. | ||
| − | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 5, p. 892|date= | + | == 2014 Update == |
| + | In 2012 the following Anabaptist denomination was active in Trinidad and Tobago: | ||
| + | <div align="center"> | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Denomination''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Congregations<br />in 2000''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Membership in<br />2000''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Congregations<br />in 2006''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Membership in<br />2006''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Congregations<br />in 2012''' | ||
| + | | align="center" style="background:#f0f0f0;"|'''Membership in<br />2012''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago | ||
| + | |style="text-align: right;" |3 | ||
| + | |style="text-align: right;" |155 | ||
| + | |style="text-align: right;" |4 | ||
| + | |style="text-align: right;" |138 | ||
| + | |style="text-align: right;" |5 | ||
| + | |style="text-align: right;" |280 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 5, p. 892|date=May 2014|a1_last=Keeler|a1_first=Richard F|a2_last= |a2_first= }} | ||
[[Category:Countries]] | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
Revision as of 04:30, 24 May 2014
Introduction
Trinidad and Tobago is a lovely tropical Caribbean twin island nation of 5,131 square kilometers (1,981 square miles) just 11 kilometers from Venezuela. Arawak and Carib Indians inhabited these islands when Christopher Columbus landed there in 1498. African and Indian slaves and indentured servants arrived in these British colonies, which became independent in 1962. A Commonwealth-type parliamentary government was retained with elections held every five years.
In 2005, the estimated population was 1,088,600 with 37.6% African-descent, 40% East Indian-descent, and 21% mixed. In terms of religion, 26% were Roman Catholic, 22.5% were Hindu, 8% were Anglican, 6% were Muslim, 3.3% did not state their religion and the rest were divided mainly into other branches of Protestantism.
Trinidad's major trading partner was the United States (petroleum, sugar) in 1986. The nation was moving from a primarily rural orientation toward an urban one, and from an agricultural society toward a technological society. Most agricultural work was still performed with hand labor, however. Primary school education was available to all children, but limited facilities and teachers did not permit all children to go on to secondary school. Part of the University of the West Indies was located in Trinidad. In the 1970s educational and health facilities and services were expanded with funds from the oil boom.
Mennonites in Trinidad and Tobago
Mennonite Church (MC) broadcasting and medical work, beginning in 1969, led to the formation of the Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago.
2014 Update
In 2012 the following Anabaptist denomination was active in Trinidad and Tobago:
| Denomination | Congregations in 2000 |
Membership in 2000 |
Congregations in 2006 |
Membership in 2006 |
Congregations in 2012 |
Membership in 2012 |
| Mennonite Church of Trinidad and Tobago | 3 | 155 | 4 | 138 | 5 | 280 |
| Author(s) | Richard F Keeler |
|---|---|
| Date Published | May 2014 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Keeler, Richard F. "Trinidad and Tobago." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. May 2014. Web. 19 Apr 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Trinidad_and_Tobago&oldid=122619.
APA style
Keeler, Richard F. (May 2014). Trinidad and Tobago. Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 19 April 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=Trinidad_and_Tobago&oldid=122619.
Adapted by permission of Herald Press, Harrisonburg, Virginia, from Mennonite Encyclopedia, Vol. 5, p. 892. All rights reserved.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.