Difference between revisions of "West Virginia (USA)"
| [checked revision] | [checked revision] |
GameoAdmin (talk | contribs) (CSV import - 20130823) |
SamSteiner (talk | contribs) (wikified table) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:West%20Virginia1.JPG|300px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Map_of_USA_WV.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] | + | [[File:West%20Virginia1.JPG|300px|thumb|right|''Source: [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Map_of_USA_WV.svg Wikipedia Commons]'']] |
| + | = Introduction = | ||
| + | West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian region of the [[United States of America|United States of America]], bordered by [[Virginia (USA)|Virginia]] on the southeast, [[Kentucky (USA)|Kentucky]] on the southwest, [[Ohio (USA)|Ohio]] on the northwest, and [[Pennsylvania (USA)|Pennsylvania]] and [[Maryland (USA)|Maryland]] on the northeast. The total area of the state is 24,230 square miles (62,755 km²) and the estimated population in 2007 was 1,812,035. In 2005, 96.01% of the population was Caucasian and 3.49% was African American. In 2001 religious affiliation was stated to be as follows: Baptist (30%); Methodist (15%); Other Protestant/General Protestant (15%); Non-denominational Christian (7%); Roman Catholic (8%); Not religious (13%); and a non-Christian religion (4%). | ||
| − | The territory of this state, located west of Virginia was a part of Virginia until 20 April 1863. On that date, West Virginia was declared a separate state by President Lincoln. This action was the result of the refusal of the northwestern counties of Virginia to accept the secession from the union decreed by the majority of the counties. | + | The territory of this state, located west of Virginia, was a part of Virginia until 20 April 1863. On that date, West Virginia was declared a separate state by President Lincoln. This action was the result of the refusal of the northwestern counties of Virginia to accept the secession from the union decreed by the majority of the counties. |
| − | + | = 1959 Article = | |
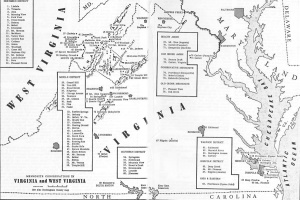
| + | [[File:ME4_830.jpg|300px|thumb|right|''Mennonite congregations in Virginia and West Virginia, 1950s.<br /> | ||
| + | Source: Mennonite Encyclopedia, v. 4, pp. 830-831. '']] | ||
| + | A few [[Mennonite Church (MC)|Mennonite Church]] (MC) families settled within the bounds of West Virginia near the close of the 18th century. These early settlements were made in Greenbrier and Rockbridge counties. Since the formation of the new state in 1863 the witness of the Shenandoah Valley Mennonite churches has been effectually brought to the people of Pendleton, Randolph, Tucker, and Hardy counties of West Virginia, which are over the mountains just across the Virginia border. In these areas there were in 1957 a total of 21 congregations, missions, or preaching points, with a total of 533 baptized members. The oldest of these was [[Salem Mennonite Church (Baker, West Virginia, USA) |Salem]] at Needmore, started in 1868, with 113 members in 1957. These congregations were all [[Virginia Mennonite Conference (Mennonite Church USA)|Virginia Conference]] and were served by the bishops of two of the Shenandoah Valley districts. -- ''Harry A. Brunk'' | ||
| − | + | = 1990 Update = | |
| − | + | The population of West Virginia declined during the 1950s through the 1980s, especially in coal mining and lumbering areas. The exodus from the highlands encouraged several Mennonite congregations to consolidate. By 1987 there were 13 Mennonite congregations in West Virginia with a total membership of 384. Eight of these congregations were affiliated with the [[Virginia Mennonite Conference (Mennonite Church USA)|Virginia Mennonite Conference]] (MC), three with [[Southeastern Mennonite Conference|Southeastern Mennonite conference]], and two with [[Allegheny Mennonite Conference (Mennonite Church USA)|Allegheny Mennonite Conference]] (MC). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Mennonites in the Appalachian regions of West Virginia have promoted craft production, a medical clinic at Harman, a campground (Harman Mountain Farm), and, for a time, a Discipleship Center (also at Harman), sponsored by [[Mennonite Board of Missions (Mennonite Church)|Mennonite Board of Missions]] ([[Mennonite Church (MC)|Mennonite Church]]). | Mennonites in the Appalachian regions of West Virginia have promoted craft production, a medical clinic at Harman, a campground (Harman Mountain Farm), and, for a time, a Discipleship Center (also at Harman), sponsored by [[Mennonite Board of Missions (Mennonite Church)|Mennonite Board of Missions]] ([[Mennonite Church (MC)|Mennonite Church]]). | ||
| − | [[Mennonite Disaster Service|Mennonite Disaster Service]] made a significant contribution following the flood disasters at Man (1971) and Petersburg (1985). -- | + | [[Mennonite Disaster Service|Mennonite Disaster Service]] made a significant contribution following the flood disasters at Man (1971) and Petersburg (1985). -- ''Paul K. Kratz'' |
| − | + | = 2009 Update = | |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin:auto" | |
| + | | align="center" colspan="3" | <strong>Anabaptist/Mennonite Groups in West Virginia, 2000</strong> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <strong>Denomination</strong> || <strong>Congregations</strong> || <strong>Adherents</strong> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Brethren In Christ Church || align="right" | 1 || align="right" | 125 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Church of the Brethren || align="right" | 80 || align="right" | 8,202 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mennonite Church USA || align="right" | 8 || align="right" | 355 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mennonite; Other Groups || align="right" | 5 || align="right" | 213 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Old Order Amish Church || align="right" | 2 || align="right" | 39 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <strong>Total</strong> || align="right" | <strong>96</strong> || align="right" | <strong>8,934</strong> | ||
| + | |} | ||
= Bibliography = | = Bibliography = | ||
ARDA: The Association of Religion Data Archives. "State Membership Report - West Virginia: Denominational Groups, 2000." [http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/54_2000.asp http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/54_2000.asp] (accessed 2 March 2009). | ARDA: The Association of Religion Data Archives. "State Membership Report - West Virginia: Denominational Groups, 2000." [http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/54_2000.asp http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/54_2000.asp] (accessed 2 March 2009). | ||
| Line 27: | Line 43: | ||
Wikipedia. "West Virginia." [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Virginia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Virginia] (accessed 1 March 2009). | Wikipedia. "West Virginia." [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Virginia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Virginia] (accessed 1 March 2009). | ||
{{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 4, pp. 929-930; vol. 5, p. 928|date=February 2009|a1_last=Brunk|a1_first=Harry A.|a2_last=Kratz|a2_first=Paul K.}} | {{GAMEO_footer|hp=Vol. 4, pp. 929-930; vol. 5, p. 928|date=February 2009|a1_last=Brunk|a1_first=Harry A.|a2_last=Kratz|a2_first=Paul K.}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Places]] | ||
| + | [[Category:States of the United States]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:46, 10 April 2020

Introduction
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian region of the United States of America, bordered by Virginia on the southeast, Kentucky on the southwest, Ohio on the northwest, and Pennsylvania and Maryland on the northeast. The total area of the state is 24,230 square miles (62,755 km²) and the estimated population in 2007 was 1,812,035. In 2005, 96.01% of the population was Caucasian and 3.49% was African American. In 2001 religious affiliation was stated to be as follows: Baptist (30%); Methodist (15%); Other Protestant/General Protestant (15%); Non-denominational Christian (7%); Roman Catholic (8%); Not religious (13%); and a non-Christian religion (4%).
The territory of this state, located west of Virginia, was a part of Virginia until 20 April 1863. On that date, West Virginia was declared a separate state by President Lincoln. This action was the result of the refusal of the northwestern counties of Virginia to accept the secession from the union decreed by the majority of the counties.
1959 Article
A few Mennonite Church (MC) families settled within the bounds of West Virginia near the close of the 18th century. These early settlements were made in Greenbrier and Rockbridge counties. Since the formation of the new state in 1863 the witness of the Shenandoah Valley Mennonite churches has been effectually brought to the people of Pendleton, Randolph, Tucker, and Hardy counties of West Virginia, which are over the mountains just across the Virginia border. In these areas there were in 1957 a total of 21 congregations, missions, or preaching points, with a total of 533 baptized members. The oldest of these was Salem at Needmore, started in 1868, with 113 members in 1957. These congregations were all Virginia Conference and were served by the bishops of two of the Shenandoah Valley districts. -- Harry A. Brunk
1990 Update
The population of West Virginia declined during the 1950s through the 1980s, especially in coal mining and lumbering areas. The exodus from the highlands encouraged several Mennonite congregations to consolidate. By 1987 there were 13 Mennonite congregations in West Virginia with a total membership of 384. Eight of these congregations were affiliated with the Virginia Mennonite Conference (MC), three with Southeastern Mennonite conference, and two with Allegheny Mennonite Conference (MC).
Mennonites in the Appalachian regions of West Virginia have promoted craft production, a medical clinic at Harman, a campground (Harman Mountain Farm), and, for a time, a Discipleship Center (also at Harman), sponsored by Mennonite Board of Missions (Mennonite Church).
Mennonite Disaster Service made a significant contribution following the flood disasters at Man (1971) and Petersburg (1985). -- Paul K. Kratz
2009 Update
| Anabaptist/Mennonite Groups in West Virginia, 2000 | ||
| Denomination | Congregations | Adherents |
| Brethren In Christ Church | 1 | 125 |
| Church of the Brethren | 80 | 8,202 |
| Mennonite Church USA | 8 | 355 |
| Mennonite; Other Groups | 5 | 213 |
| Old Order Amish Church | 2 | 39 |
| Total | 96 | 8,934 |
Bibliography
ARDA: The Association of Religion Data Archives. "State Membership Report - West Virginia: Denominational Groups, 2000." http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/54_2000.asp (accessed 2 March 2009).
Horsch, James E., ed. Mennonite Yearbook and Directory. Scottdale: Mennonite Publishing House, 1988-89: 44.
Wikipedia. "West Virginia." http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/West_Virginia (accessed 1 March 2009).
| Author(s) | Harry A. Brunk |
|---|---|
| Paul K. Kratz | |
| Date Published | February 2009 |
Cite This Article
MLA style
Brunk, Harry A. and Paul K. Kratz. "West Virginia (USA)." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. February 2009. Web. 16 Apr 2024. https://gameo.org/index.php?title=West_Virginia_(USA)&oldid=167562.
APA style
Brunk, Harry A. and Paul K. Kratz. (February 2009). West Virginia (USA). Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. Retrieved 16 April 2024, from https://gameo.org/index.php?title=West_Virginia_(USA)&oldid=167562.
Adapted by permission of Herald Press, Harrisonburg, Virginia, from Mennonite Encyclopedia, Vol. 4, pp. 929-930; vol. 5, p. 928. All rights reserved.
©1996-2024 by the Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia Online. All rights reserved.